Facts About Kaaba in Makkah

The Kaaba holds a pivotal place in the hearts of millions of Muslims around the world. Situated in the center of the Grand Mosque in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, it is not merely a building; it is the qibla (direction of prayer) for Muslims and a symbol of unity and faith. This article delves into numerous intriguing facts about the Kaaba in Makkah that illuminate its significance, history, and impact on the Islamic world.
The Historical Significance of the Kaaba
The history of the Kaaba is as profound as its spiritual significance. Here are some key historical facts:
- Origins: Believed to have been built by the Prophets Ibrahim (Abraham) and his son Ismail (Ishmael), the Kaaba was established as a sanctuary dedicated to the worship of the One God.
- Historical Changes: Over centuries, the Kaaba has undergone multiple renovations. The current structure was reconstructed entirely in the early 1990s, utilizing the finest marble and materials from around the world.
- Hajj Rituals: The Kaaba is the focal point during the annual pilgrimage of Hajj, drawing millions of Muslims to perform rituals, including the Tawaf, where pilgrims circumambulate the Kaaba seven times.
Architectural Features of the Kaaba
The Kaaba’s architecture is striking and purposefully designed to create an environment of spiritual reflection. Key architectural facts include:
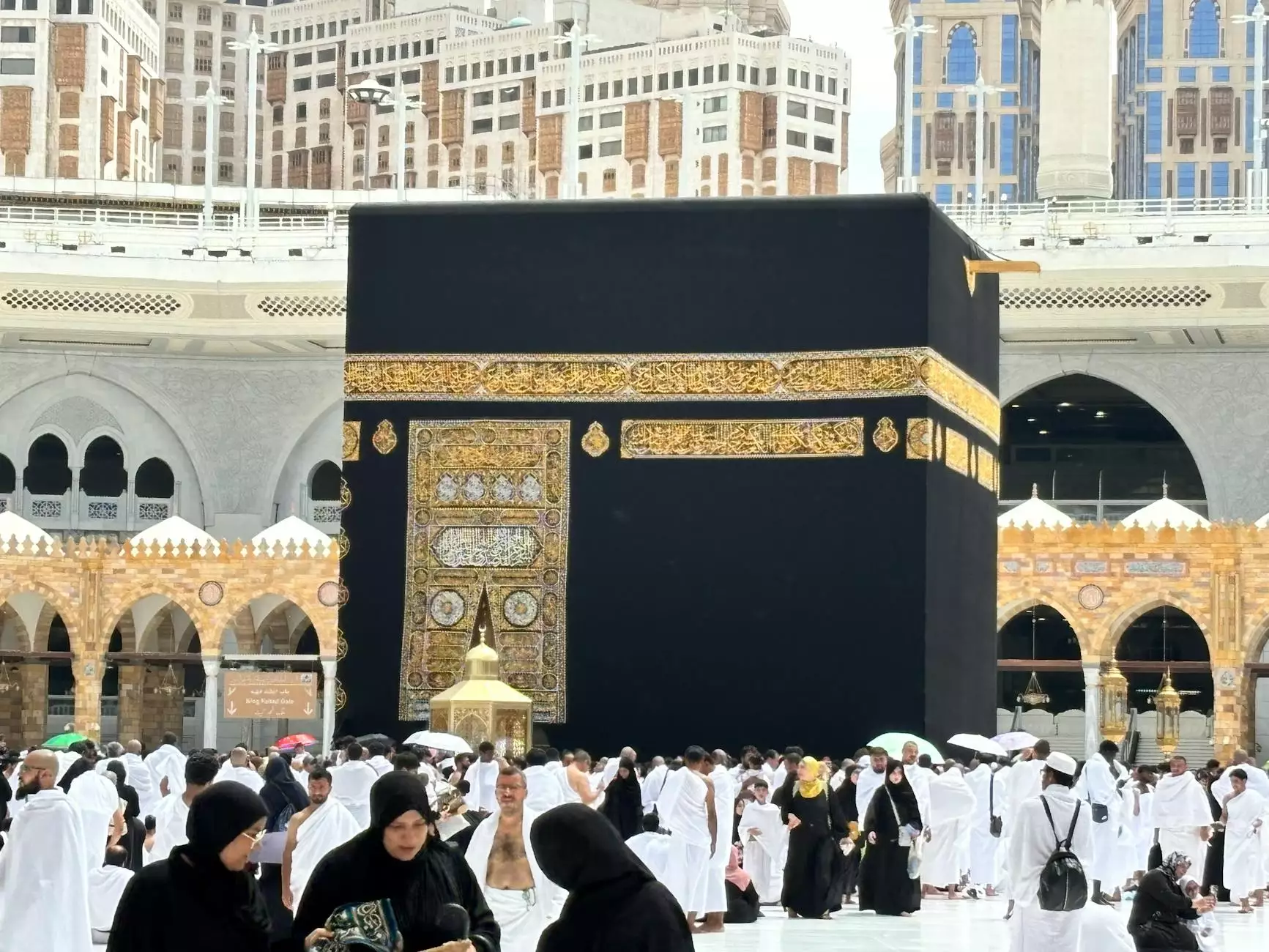
- Dimensions: The Kaaba is a cuboid structure measuring approximately 13.1 meters in height, with a length of 11 meters and a width of 12 meters.
- Black Stone: Embedded in the eastern corner, the Black Stone (Hajr al-Aswad) is a significant artifact, believed to have originated from heaven. Pilgrims often strive to kiss or touch it during their worship.
- Covering (Kiswah): The Kaaba is draped in a black silk cloth known as the Kiswah, embroidered with verses from the Quran in gold thread. This covering is changed annually during the Hajj.
The Spiritual Role of the Kaaba
For Muslims, the Kaaba is much more than just an architectural marvel; it represents the spiritual heart of Islam. Here are some essential insights:
- Unity of Direction: The Kaaba serves as a unifying point for Muslim prayer worldwide. Regardless of where a Muslim is located, they turn towards the Kaaba during their five daily prayers.
- Symbol of Faith: As one of the most sacred sites in Islam, it symbolizes submission to Allah and signifies the importance of faith in the everyday lives of Muslims.
- Spiritual Cleansing: The rituals performed during Hajj, particularly those centered around the Kaaba, are believed to purify sins and reaffirm one’s commitment to Allah.
Significant Events Associated with the Kaaba
Throughout history, the Kaaba has witnessed numerous significant events that have shaped Islamic traditions and practices. Here are some noteworthy events:
- Pre-Islamic Era: The Kaaba was a hub of various tribal deities before the advent of Islam, symbolizing the region's diverse spiritual landscape.
- Conquest of Makkah: In 630 CE, Prophet Muhammad and his followers peacefully conquered Makkah, reinstating the Kaaba as a place of monotheistic worship.
- Historical Document: The Treaty of Hudaybiyyah in 628 CE was significant as it allowed Muslims to return to Makkah, emphasizing the importance of the Kaaba in community relations.
Modern-Day Relevance of the Kaaba
In contemporary times, the Kaaba continues to hold immense relevance in the lives of Muslims and has become a focal point for various global events:
- Tourism and Economy: The influx of pilgrims visiting Makkah generates significant economic activity, impacting local businesses and the broader Saudi economy.
- Global Community: The Kaaba serves as a reminder of the global Muslim community (Ummah), fostering solidarity and a shared sense of purpose among believers worldwide.
- Interfaith Dialogues: The Kaaba has also become a point of interest for interfaith dialogues, emphasizing shared values of spirituality and worship among different religions.
Contemporary Challenges and Preservation
As the number of pilgrims continues to rise, the sanctity and preservation of the Kaaba face various challenges:
- Infrastructure Development: To accommodate millions of annual visitors, ongoing construction projects have been initiated, which raises questions about maintaining the historical integrity of the site.
- Environmental Concerns: The increasing pollution and environmental degradation around Makkah necessitate efforts to protect and preserve this holy site.
- Security Measures: In recent years, enhancing security measures during Hajj has become paramount to ensure the safety of pilgrims and the integrity of the Kaaba.
The Kaaba and Its Symbolism in Islamic Culture
The Kaaba transcends its physical presence and embodies profound symbolism in Islamic culture:
- The Five Pillars of Islam: The importance of the Kaaba is highlighted in the Hajj, one of the Five Pillars of Islam, representing faith, dedication, and community.
- Cultural Artifacts: The Kaaba serves as inspiration for various cultural artifacts, including poetry, art, and literature, illustrating its omnipresence in Islamic expression.
- Spiritual Transformation: Many Muslims describe their pilgrimage to the Kaaba as a transformative experience that deepens their faith and commitment to Islamic teachings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Kaaba in Makkah is a profound symbol of faith, history, and unity for Muslims around the world. Its architectural beauty, rich history, and spiritual significance make it an enduring cornerstone of Islamic practice and belief. As millions continue to turn towards the Kaaba in prayer, it remains a vital aspect of both individual faith and the collective identity of the Muslim community. Whether you are planning your pilgrimage or simply looking to learn more, understanding the myriad facts about the Kaaba will deepen your appreciation for this sacred monument.
facts about kaaba in makkah