The Sweet Success of Sugar Production in Brazil
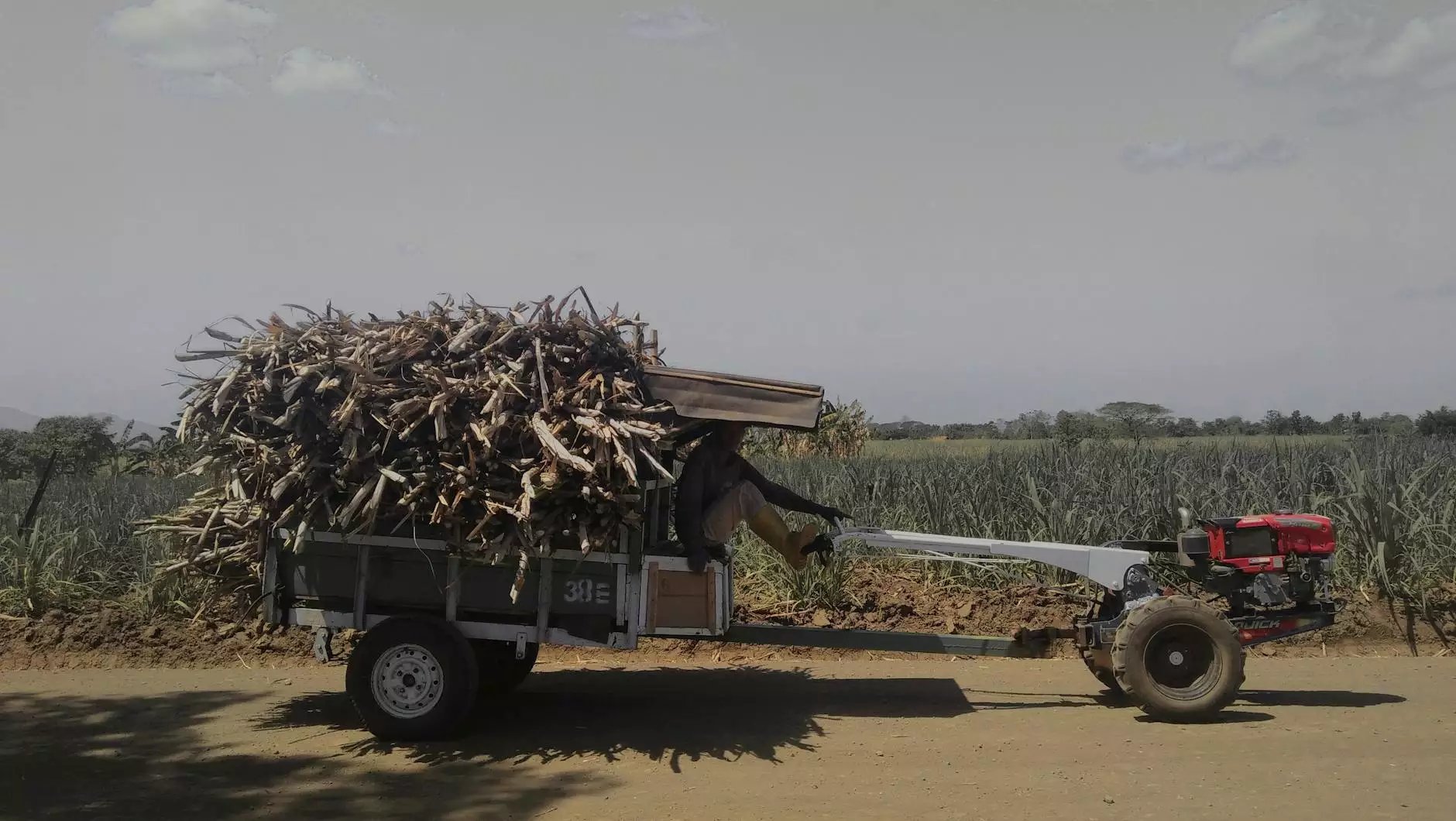

Brazil stands out as the world's largest sugar producer and exporter, contributing significantly to the global sugar market. With its favorable climate, vast arable land, and advanced agricultural techniques, the country has established itself as a powerhouse in sugar production. This article delves into the intricacies of the sugar industry in Brazil, exploring its history, production methods, market trends, and the key players that dominate this vibrant sector.
The History of Sugar Production in Brazil
The story of sugar in Brazil dates back to the 16th century when sugarcane was first introduced by Portuguese colonizers. The favorable climate of the northeastern region of Brazil, particularly around Pernambuco, facilitated the growth of sugarcane, leading to the establishment of numerous sugar mills, known as engenhos.
Over the centuries, Brazil developed a robust sugar industry that has evolved amid changing global demands. By the 19th century, Brazil had become the leading producer of sugar, leveraging slave labor, and thereafter transitioning to more modern labor practices in the 20th century. With technological advancements and the globalization of trade, the Brazilian sugar industry continues to grow, influencing economies worldwide.
Why Brazil is a Leading Sugar Producer
Brazil's superiority in sugar production can be attributed to various factors:
- Favorable Climate: Brazil's climate is optimal for sugarcane cultivation, with abundant sunlight and adequate rainfall.
- Advanced Technology: Brazilian sugar producers utilize state-of-the-art agricultural techniques and machinery to maximize yield and efficiency.
- Extensive Land Resources: Brazil boasts vast expanses of arable land, particularly in regions like São Paulo, Goiás, and Minas Gerais.
- Government Support: The Brazilian government provides incentives for sugarcane farming and investment in biofuels, further expanding the industry.
- Export Opportunities: As a major exporter, Brazil supplies sugar to many countries, ensuring stable demand and fostering global trade relations.
The Sugar Production Process in Brazil
The process of sugar production in Brazil involves several critical stages:
1. Cultivation of Sugarcane
The journey begins with the cultivation of high-quality sugarcane. Farmers select suitable varieties that yield high sugar content and resist diseases. The land is prepared through soil tilling, and sugarcane is typically planted between February and March to ensure optimal growth before harvest.
2. Harvesting
Harvesting sugarcane in Brazil is a highly mechanized process, allowing for efficiency and speed. Modern harvesters cut the sugarcane stalks close to the ground and collect them without damaging the plant. This step is critical, as it ensures that the highest quality cane is processed.
3. Processing
Once harvested, sugarcane is transported to processing facilities where it undergoes crushing to extract juice from the stalks. This juice is then clarified, evaporated, and crystallized to produce raw sugar. The refining process may include further purification, resulting in granulated white sugar.
4. Quality Control
Quality control is paramount in sugar production. Brazilian producers adhere to strict standards to ensure that their sugar meets international quality benchmarks. This includes testing for sugar content, color, and purity.
5. Packaging and Distribution
After quality checks, sugar is packaged and prepared for export. Brazil's logistical infrastructure supports the efficient distribution of sugar both domestically and internationally, making it accessible to consumers and businesses worldwide.
Market Dynamics of Sugar in Brazil
The Brazilian sugar market is characterized by several robust factors:
Global Demand
With increasing global demand for sugar for food production, beverages, and biofuels, Brazil plays a crucial role in meeting this demand. The country's sugar is not only consumed domestically but also exported to key markets in Europe, Africa, and Asia.
Market Competition
Brazilian sugar producers face competition locally and globally. To maintain a competitive edge, they focus on innovation, sustainable practices, and expanding their market reach.
Pricing and Trade Policies
The price of sugar is influenced by international market conditions, government policies, and climate factors. Brazil benefits from favorable trade agreements that enhance its export capabilities.
Environmental Considerations
As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, Brazilian sugar producers are adopting sustainable farming practices. This includes minimizing pesticide use, implementing efficient water management systems, and exploring biofuel production from sugarcane by-products.
Key Players in the Brazilian Sugar Industry
The sugar industry in Brazil is composed of several major corporations that dominate production:
- Cosan: One of the largest producers, involved in both sugarcane and biofuels, operating globally.
- Raízen: A joint venture between Shell and Cosan, Raízen is a leader in sugar, ethanol, and energy production.
- São Martinho: One of the largest sugar and ethanol producers, known for its commitment to sustainable practices.
- Grupo Tereos: A major player focused on sugar and ethanol production, with significant investments in technology.
- JBS: While primarily known for meat production, JBS also has a stake in sugar production, leveraging its extensive supply chain.
Challenges Facing the Sugar Industry in Brazil
Despite its strengths, the Brazilian sugar industry faces various challenges:
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to agriculture globally, including Brazil's sugarcane fields. Increased temperature and unpredictable weather patterns could affect crop yields and quality.
Trade Regulations
Changes in international trade policies and tariffs can impact the competitive landscape for Brazilian sugar exports, requiring producers to stay adaptable and informed.
Labor Shortages
As mechanization continues to advance, there is increasing concern about labor shortages in the agricultural sector. Balancing technology with human resources is critical for sustained production.
Health Trends
Growing health consciousness around sugar consumption can influence demand patterns, pushing producers to explore alternatives and sugar substitutes.
Future Prospects for Brazilian Sugar
Looking forward, the future of sugar production in Brazil appears promising, with several trends shaping the industry:
Technological Advancements
Continued investment in technology and innovation will lead to improved production methods, enhancing both yield and sustainability. Precision agriculture and genetic modifications are key areas of focus.
Expansion into Biofuels
With a global shift towards renewable energy, Brazilian sugar producers are increasingly investing in ethanol production from sugarcane, creating new revenue streams and reducing carbon footprints.
Sustainability Initiatives
Producers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices to attract environmentally conscious consumers. Emphasizing organic and fair-trade practices will become crucial for maintaining market share.
Conclusion
In summary, Brazil's position as the world's leading sugar producer is the result of a rich history, strategic advantages, and continuous innovation. The industry is poised for growth, adapting to challenges while embracing sustainability and technological advancements. For businesses and investors, the Brazilian sugar market represents abundant opportunities to tap into a lucrative sector with global implications.
As the demand for sugar continues to rise in both traditional and new markets, understanding the nuances of production and distribution in Brazil can pave the way for success. Whether you are a supplier, manufacturer, or stakeholder in the sugar industry, aligning with Brazilian producers can open doors to a sweet future.
sugar producer brazil